What is compound interest and simple interest? How do you calculate principal and compound interest? It is the result of reinvesting interest, rather than paying it out, so that interest in the next period is then earned on the principal sum plus previously accumulated interest.
The longer you can leave your money untouche the greater it can grow, because compound interest grows exponentially over time. Even if you never made another deposit after that time, after years.
Some forms of lending may also be subject to compound interest, including some credit cards and loans – meaning you’ll owe interest on the interest you’ve previously accrued. Multiply the principal amount by one plus the annual interest rate to the power of the number of compound periods to get a combined figure for principal and compound interest. Compound interest doesn’t just apply to savings.
Subtract the principal if you want just the compound interest. Put simply, compound interest changes the amount of.
The compound interest formula is an equation that lets you estimate how much you will earn with your savings account. The formula for annual compound interest is as.
Determine how much your money can grow using the power of compound interest. Money handed over to a fraudster won’t grow and won’t likely be recouped. So before committing any money to an investment opportunity, use the “Check Out Your Investment Professional” search tool below the calculator to find out if you’re dealing with a registered investment professional. Because of this, accounts with compound interest grow faster than those with simple interest.
For example, if your interest compounds annually, that means that you’ll gain more interest in the. It is the basis of everything from a personal savings plan to the long term growth of the stock market.
The concept of compound interest can sound a bit technical and confusing, but in a nutshell, it means earning interest on your interest. In the long term, it can make a significant difference for your savings – as long as you keep putting aside both your savings and your interest.
On the other han compound interest is interest earned on both the principal and on the accumulated interest. Because interest is also earned on interest, earnings compound over time like an exponentially-growing, avalanching snowball.
With compound interest, the interest earned over time will continue to increase as long as no money is withdrawn from the account. This is because all previously earnt interest remains in the account so the sum from which to calculate interest becomes larger over time. Visit the post for more. If you are not that familiar with equations, you do not need to worry about trying to plug in all the numbers.
So, whereas with the interest compounded you would earn £218. Now that you know how compounding works, you can search for a savings account that allows you to use “the most powerful force in the universe” while also giving you a competitive rate, so you can make the most of interest stacking upon.
Find out how making small payments over a long period of time could make you rich. Amy’s story – an example to show how compound interest works. To show you how compound interest affects a balance over time, we’re going to use a made-up example based on Amy borrowing £0at a simple interest rate of 12%. For the sake of the example, let’s say that Amy doesn’t pay anything back for months.
However, the principal amount will. The AER assumes your interest rate based on if you were to leave your money in the savings account for a year, and it also factors in the compound interest. As a result, when you look at the monthly interest paid by an account the AER shown will be higher than the gross rate.
Sadly, compound interest tends to have an even bigger impact on debts than on savings, because interest rates are higher. So, the compound interest is the interest on interest. The interest of each year or some fixed time period is added to the principal sum and the new amount becomes the principal for the next year and interest is calculated on the increased amount for the next year.
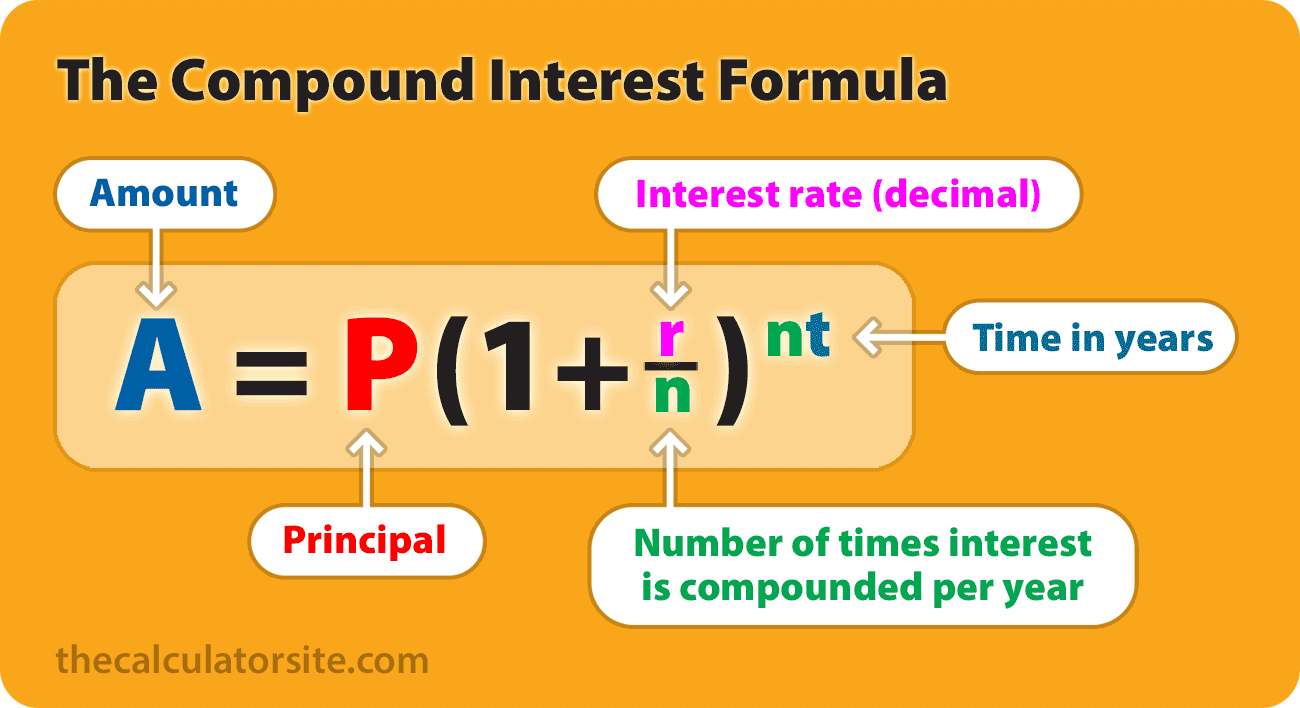
Calculate compound interest on an investment or savings. For this formula, P is the principal amount, r is the rate of interest per annum, n denotes the number of times in a year the interest gets compounded, and t denotes the number of years.

It is the outcome of reinvesting interest, rather than paying it out, so that interest in the next period is earned on the principal sum plus previously accumulated interest. Think of compounding interest like a snowball, as you roll it down a hill, it gradually becomes bigger and bigger, with the total mass (amount of money) increasing its size more and more each time. A lesson on compound interest.
It includes a resource from maths box and a quizizz that I’ve created with the questions minimally increasingly difficult.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.